深入了解植酸和膳食纤维等不可消化成分及其在家禽饲料中的相互作用,是获取外源酶全部价值的关键。为了估算酶制剂在动物饲料中的潜力,营养学家必须首先了解有多少营养成分未被消化并具有抗营养特性。由于外源酶的目的是将部分非消化成分释放为可消化的营养物质,因此了解非消化营养物质的数量有助于评估这种酶反应的潜力。事实证明,将几种外源酶视为一种独特的酶解决方案,可分解反营养成分并从中释放营养物质,是评估饲料消化率改善情况的最佳方法。这种观点被称为饲料酶方法。Feedase是指考虑整个饲料的整体酶解,从而提高所有营养物质的消化率,包括脂肪、淀粉、蛋白质、磷等......在这种新方法中,酶的作用与特定底物相关,但酶的作用与对营养物质(如脂肪、淀粉、蛋白质、磷)的间接作用相关,与酶的互补作用相关。
为验证多糖酶制剂(Rovabio Advance®)的功效,在法国安迪苏 实验场对13-22日龄的Ross PM3公肉鸡进行了消化率试验。试验采用欧洲标准方法,实施自由采食,并收集3天总排泄物(Bourdillon et al., 1990)。 0-12 日龄期间,鸡只食用以小麦和大豆为基础的普通碎粒型初生雏鸡饲料;随后喂食成分简单的生长料(小麦和大豆粉)或成分更复杂的生长料(小麦、大麦、黑麦、小麦干酒糟、大豆粉、葵花籽粉、油菜籽粉)。 无论饲料成分如何,添加该酶显著提高了能量利用率和多种营养素的消化率(表1)。
| 饲料类型 | 简单 | 复杂 |
|---|---|---|
| 营养消化率和能量利用率 | ||
| 营养消化率和能量利用率 | ||
| 体重增加(克 | -2.4% | +2.0% |
| 饲料摄入量,克 | -3.5% | -4.3% |
| 饲料转换 | -1.4% | -6.0% |
| 干物质,% | +4.0%* | +7.8%* |
| 可溶性有机物,% | +3.4%* | +10.9%* |
| AME, 千卡/千克 | +3.5%*(+107 千卡/千克) | +8.2%*(+228 千卡/千克) |
| AME, 兆焦耳/千克 | +3.5%*(+0.45 兆焦/千克) | +8.2%*(0.95 兆焦耳/千克) |
| 蛋白质,% | +4.2% | +11.2%* |
| 脂肪,% | +2.5% | +17.4%* |
| 淀粉,% | +3.7%* | +3.8%* |
| 灰分,% | +10.3%* | +13.4%* |
| 钙,% | +1.0% | +7.2%* |
| 磷,% | +2.4% | +5.9%* |
*p<0.051 Rovabio® Advance L2
Ref: Cozannet et al. 2017, Poultry Science
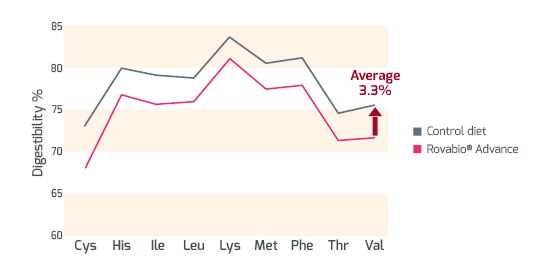
This improvement was more important for the complex diets than for the simple diet. The improvement observed on energy utilization and digestibility of nutrients was related with arabinose xylose content 69.2 vs. 59.5 g/kg for complex and simple diets, respectively. To further validate the concept of global feed digestibility, the effect of Rovabio® Advance was evaluated in a standard wheat-based diet diluted with 3% of sand (Cozannet et al. 2018, Journal of Poultry Science). This study investigated the effect of Rovabio Advance® on energy and ileal amino acid (AA) digestibility of a complete wheat/soybean-based diet in broilers. The commercial control diet was compared with a 3% nutrient-diluted version using silica as inert diluent. Digestibility of dry matter (DM), AA and gross energy (GE) were determined by analysis of feed, excreta and digesta. Ross PM3 broiler chicks were studied during the grower period and diet dilution did not increase feed intake. Fecal energy digestibility was similar (approximating 73%) for diets without enzymes (P = 0.99). However, apparent metabolizable energy (AME) content was significantly lower in the diluted versus control diet. Rovabio® Advance improved energy utilization (P < 0.001), leading to an increase of AME content for both the diluted and standard diets. AME content of diluted diet with Rovabio Advance was similar to that of the standard diet without enzymes (P = 0.98), demonstrating the ability of this enzyme to fully compensate the 3% nutrient dilution (Figure 1).

At ileal level, AA digestibility was around 75% across all treatments. The addition of the multi-carbohydrase increased AA digestibility by an average of 3.3% (P<0.001, Figure 2). Rovabio Advance® restored nutrient availability when the nutrient content of a diet was diluted by 3%. This study highlights the importance of considering the entire nutrient matrix when global enzyme solutions are supplemented to diets.
为了评估一种含有多种碳水化合物酶(特异性木聚糖酶、β-葡聚糖酶和阿拉伯呋喃糖苷酶)和最佳剂量植酸酶(1000 FTU/公斤饲料)的复合酶的效果,这种酶被称为 Rovabio®Advance Phy在法国 Zootests 进行了一项肉鸡栏试验。与阳性对照相比,试验日粮的配方规格较低(表 2)。
| 玉米和小麦膳食 | 与 PC 相比的降低率 | 减少量,单位 % 对比 PC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ME | 挖。AA | AvP | Ca | |
| NC1 | 3 | 3 | 0.174 | 0.157 |
| NC2 | 4 | 4.5 | 0.174 | 0.157 |
| NC3 | 5 | 6 | 0.174 | 0.157 |
ME was reduced by 3, 4 or 5% and dAA by 3, 4.5 or 6%, in 3 different treatments, along with a fixed reduction of 0.174% units avP and 0.157% units Ca. These three groups were compared with or without the multi-carbohydrase phytase complex (MCPC). A positive control was raised in parallel. All treatments used a corn wheat-soybean based diets. Growth performance, carcass characteristics and bone mineralization were measured, and results statistically compared. The reduction of ME, dAA, avP and Ca in the diet significantly reduced the body weight gain and increased FCR (P < 0.0001; Figure 3) similarly for the 3 NC diets; with no effect on feed intake.

在42日龄时,通过添加该酶制剂,无论是否调整日粮配方,这些生产性能指标均恢复至阳性对照组水平。 本试验证明Advance Phy 肉鸡Advance Phy 添加Advance Phy 可显著降低营养配比要求:代谢能(ME)降低5%、必需氨基酸(dAA)降低6%、促排卵肽(avP)降低0.174%单位、钙(Ca)降低0.157%单位。研究表明该酶制剂组合能有效降低饲料成本。
使用 替代成分由于基质数量较多,它们对酶非常敏感,因此使用它们似乎是降低成本的一种有前途的策略。它们的低消化率可以通过添加酶来弥补,而且可以提供不可忽略的营养成分。在含有 6% 葵花籽粕的玉米-大豆-小麦日粮中,Rovabio®Advance Phy 可以节省多达 27 欧元/吨的饲料,而不会对动物的生产性能产生任何影响。
作者:Pierre Cozannet 博士和安迪苏饲料消化专家 Maamer Jlali 博士
Jlali 等人(2020 年)。评估肉鸡日粮中的多淀粉酶和植酸酶复合物的能量、氨基酸、可利用磷和钙含量。家畜科学 241 (2020) 104227。
产品名称和供应情况可能因地区而异,详情请联系当地 Adisseo 代表。
请输入您的电子邮件,只需登录一次即可访问所有内容并进行下载。

产品名称和供应情况可能因地区而异,详情请联系当地 Adisseo 代表。
用作饲料原料的谷物含有难以消化的碎纤维,会降低饲料的消化率。分解这些成分需要在饲料中添加特定的酶。这对于避免宝贵营养成分的损失及其对经济和环境的影响至关重要。
Rovabio® 是一系列酶制剂解决方案,可提高动物、家禽和猪对植物性饲料的消化率。Rovabio® 在节约成本、提高动物生产性能的同时,还有助于改善饲养环境,提高可持续性。
如果您想进一步了解我们的酶制剂解决方案,请点击下面的相关按钮。